Temporary Pacemakers: Understanding, Function, and Importance in Cardiac Care
Temporary pacemakers serve as critical devices in managing cardiac arrhythmias, providing temporary electrical stimulation to regulate the heart’s rhythm. These devices play a vital role in stabilizing heart rate and ensuring adequate blood flow, especially in emergency situations or during post-operative care. Let’s explore the intricacies, functions, and significance of temporary pacemakers in the realm of cardiac health.
What are Temporary Pacemakers?
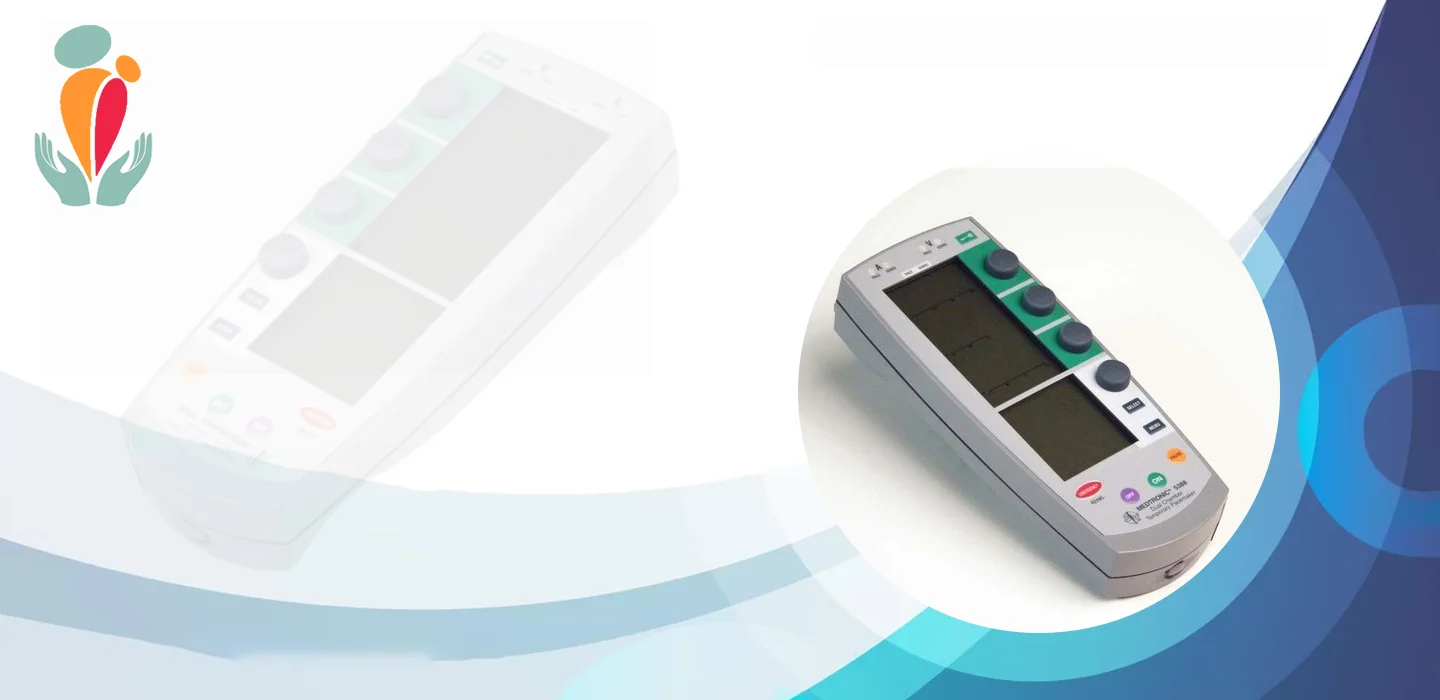
Temporary pacemakers are medical devices designed to manage abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) by delivering electrical impulses to the heart. Unlike permanent pacemakers, which are surgically implanted, temporary pacemakers are used on a short-term basis to provide immediate pacing support until the underlying heart condition stabilizes or a permanent solution is determined.
How Temporary Pacemakers Work
– Electrical Stimulation: These devices consist of wires (leads) connected to the heart, delivering electrical signals to regulate the heart’s rhythm. The pacing rate and strength can be adjusted based on the patient’s needs.
– Indications for Use: Temporary pacemakers are often employed in emergency situations, such as severe bradycardia (slow heart rate), heart block, or during post-operative recovery to maintain a steady heartbeat.
Types of Temporary Pacemakers
1. Transcutaneous Pacemakers: These external devices deliver electrical impulses through pads placed on the skin’s surface, providing temporary pacing until a more permanent solution is available.
2. Transvenous Pacemakers: Inserted through a vein, these temporary pacemakers have leads positioned directly into the heart, offering more precise and efficient pacing.
Importance in Cardiac Care
– Critical Emergency Intervention: Temporary pacemakers are crucial in emergency situations where prompt intervention is required to stabilize the heart rate and prevent life-threatening complications.
– Post-Surgery Support: They are utilized post-operatively to manage arrhythmias that may arise following cardiac procedures, ensuring the patient’s heart remains stable during recovery.
– Bridge to Permanent Solution: Act as a bridge until a permanent pacemaker can be implanted or until the underlying condition resolves, ensuring continuous cardiac support.
– Versatile and Adjustable: These devices offer flexibility in adjusting pacing parameters, accommodating individual patient needs and responding effectively to changes in heart rhythm.
Understanding Temporary Pacemakers:
Are external or internal devices used to regulate the heart rate and rhythm on a short-term basis. Unlike permanent pacemakers, which are surgically implanted for long-term use, temporary pacemakers are typically employed in acute settings, such as during cardiac surgery, post-operative recovery, or in emergency situations.
Function of Temporary Pacemakers:
- Electrical Stimulation: Deliver electrical impulses to the heart muscle, initiating depolarization and contraction of the cardiac chambers. These impulses override the heart’s intrinsic electrical activity, ensuring that the heart beats at a predetermined rate and rhythm.
- Rate Control: Allow healthcare providers to control the heart rate by adjusting the pacing parameters, including the pacing rate (beats per minute) and pacing mode (e.g., demand pacing or fixed-rate pacing).
- Rhythm Management: Can help manage various heart rhythm disturbances, including bradycardia (slow heart rate), heart block, atrioventricular (AV) node dysfunction, and tachy-brady syndrome.
Importance in Cardiac Care:
- Emergency Interventions: Are used as emergency interventions to stabilize patients with life-threatening bradyarrhythmias, such as complete heart block or symptomatic bradycardia. Prompt initiation of temporary pacing can prevent hemodynamic compromise and improve patient outcomes.
- Support During Surgery: Are frequently utilized during cardiac surgery, especially procedures involving the heart’s conduction system (e.g., valve surgery, coronary artery bypass grafting). They provide temporary cardiac pacing support during and after surgery until the patient’s intrinsic conduction recovers.
- Post-Operative Recovery: After cardiac surgery or interventions, patients may experience transient conduction abnormalities or hemodynamic instability. Temporary pacemakers offer critical support during the post-operative recovery period, ensuring adequate heart rate and rhythm until the patient’s cardiac function stabilizes.
- Bridge to Permanent Pacing: In some cases, temporary pacemakers serve as a bridge to permanent pacing, providing interim support until a permanent pacemaker can be implanted. This is particularly relevant for patients with reversible causes of bradyarrhythmias or those awaiting elective pacemaker implantation.
Conclusion:
Temporary pacemakers play a pivotal role in cardiac care, providing essential support for patients with heart rhythm abnormalities or conduction disorders. Understanding their function and importance is crucial for healthcare providers involved in the management of cardiac conditions, including cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, anesthesiologists, and critical care teams.
As temporary pacemakers continue to evolve with advancements in technology and clinical practice, they remain invaluable tools in the armamentarium of cardiac care, offering life-saving interventions and improving outcomes for patients with acute and chronic cardiac conditions. Through their timely deployment and effective management, temporary pacemakers contribute to the delivery of optimal cardiac care and the preservation of cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, temporary pacemakers play an instrumental role in managing cardiac arrhythmias, providing immediate and crucial support in emergencies and post-operative care. Their versatility and ability to stabilize heart rhythms highlight their significance in ensuring optimal cardiac function, underscoring their vital role in cardiac healthcare.





Add comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.